Indian Navy
Indian Armed Forces
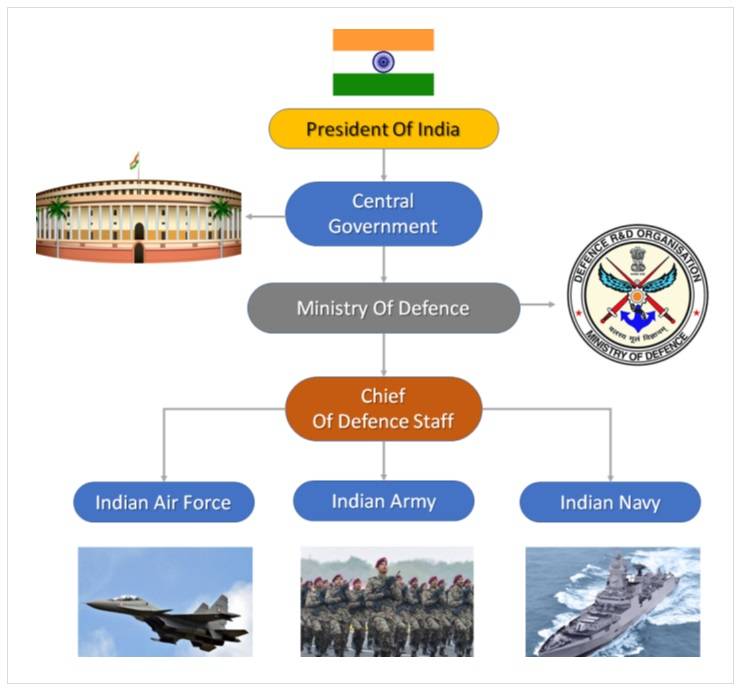
The Indian Navy is ranked seventh in the world in terms of combat strength. It is an Indian Armed Forces maritime branch. The Supreme Commander of the Indian Navy is the President of India. The Indian navy is headed by a four-star admiral designated as the Chief of Naval Staff, who operationally commands the navy.
It possesses the combat capabilities of a blue-water navy and operates in the Persian Gulf Region, the Horn of Africa, and the Malacca Strait. It also conducts anti-piracy operations on a regular basis and collaborates with other navies in the region.
The Indian navy is mainly responsible for safeguarding India’s maritime borders. It actively collaborates with other Indian armed forces, which include the Indian army and the Indian Air Force.
It has naval warfare capabilities to act as a formidable deterrent or defeat any internal as well as external threats or aggression against the territory, people, or maritime interests of India, both in war and peace.
The Navy actively conducts joint exercises with friendly countries, goodwill visits, and humanitarian missions, including disaster relief. The Navy’s goodwill visits help to promote bilateral relations between nations.
The Indian Navy’s combat strength includes 67,252 active and 75,000 reserve personnel in service. It has a fleet size of 150 ships, submarines, and dedicated 300 aircraft for combat and non-combat operations.

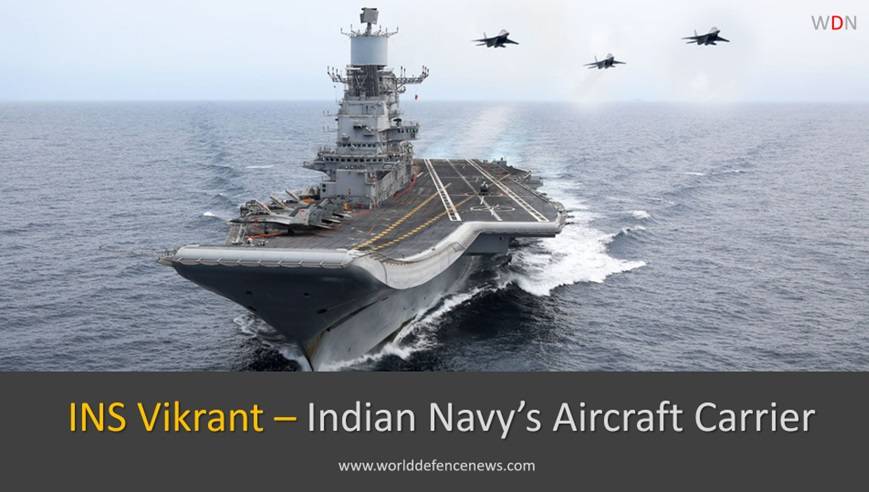
The operational fleet of the navy also consists of 2 operational aircraft carriers ( INS Vikramaditya And INS Vikrant ) and 1 amphibious transport dock, 8 landing ship tanks, 10 destroyers, 13 frigates, 2 ballistic missile submarines, 16 conventionally-powered attack submarines, 24 corvettes, one mine countermeasure vessel, 4 fleet tankers, and numerous other auxiliary vessels, small patrol boats, and other sophisticated ships.
Indian Navy General Information
The British Indian Navy was first founded on 5th September 1612 during the British rule over India. The Indian navy was founded on the 26th of January 1950, after India’s independence, marked by the end of colonial British rule. Army Day is celebrated every year on the 4th of December.
Indian Navy | Details | |
Royal British Indian Navy Founded On | 5th September 1612 | |
Indian Army Founded On | 26th January 1950 | |
Indian Navy Active Personnel | 67,252 | |
Indian Navy Reserve Personnel | 75,000 | |
Commander In Chief | President Of India | |
Chief Of The Naval Staff | Admiral R. Hari Kumar | |
Indian Navy Day | 4th December Every Year | |
Indian Navy Fleet Size | Indian Navy Combat Ships - 150 Indian Navy Support Ships - 145 |
Source – Indian Navy
Indian Navy Fleet Size
Indian Navy Weapons Strength
The Indian navy’s weapons and naval ships inventory includes different types of combat ships and support vessels. The Indian Navy’s combat ships include aircraft carriers, destroyers, frigates, corvettes, submarines, nuclear powered submarines, offshore patrol vessels, patrol vessels, high speed patrol boats, training ships, research vessels, landing ships and other support vessels.
Source – Indian Navy
Indian Navy Organization
Indian Navy Command Head Quarters
The Indian Navy is a well-balanced and cohesive three-dimensional force, capable of operating above, on, and under the surface of the oceans, efficiently safeguarding our national interests.
The Chief of the Naval Staff (CNS) exercises operational and administrative control of the Indian Navy from the Integrated Headquarters of the Ministry of Defence (Navy).
The Chief of the Naval Staff is assisted by the Vice Chief of the Naval Staff (VCNS) and three other principal staff officers, namely the Deputy Chief of the Naval Staff (DCNS), the Chief of Personnel (COP), and the Chief of Material (COM).
Source – Indian Navy
Disclaimer
This page is not a official website of the Indian Navy. The link to the official Indian Navy page is mentioned in the references. The information compiled on this page is only for education purpose.






















