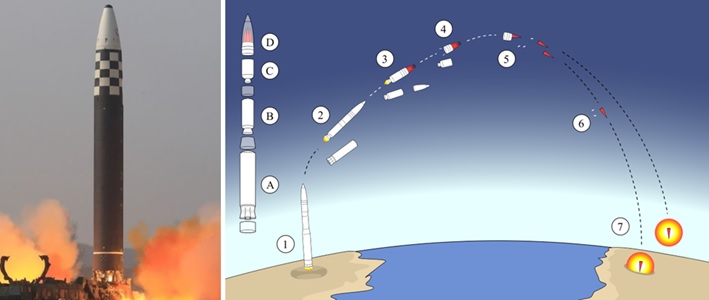
Indian BMD Program
Indian Ballistic Missile Defence (BMD) Program By DRDO To Develop Protective Shield Against ICBM Missile Attack.
Indian BMD program is a Ballistic Missile Defence (BMD) shield developed by DRDO to protect Indian cities and strategically vital installations against ICBM Missile attack.
The Indian Ballistic Missile Defence (BMD) program is a strategically important program for the Indian government of India. The main objective of the BMD program is to developing and deploying a multi-layered ballistic missile defense system to protect India from potential ICBM missile attacks.
The Indian BMD program is being developed by the Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO) in collaboration with other Indian defense agencies. The BMD program was under development for a long time. The program got impetus and was put on the fast-track BJP government came into power led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in year 2014.
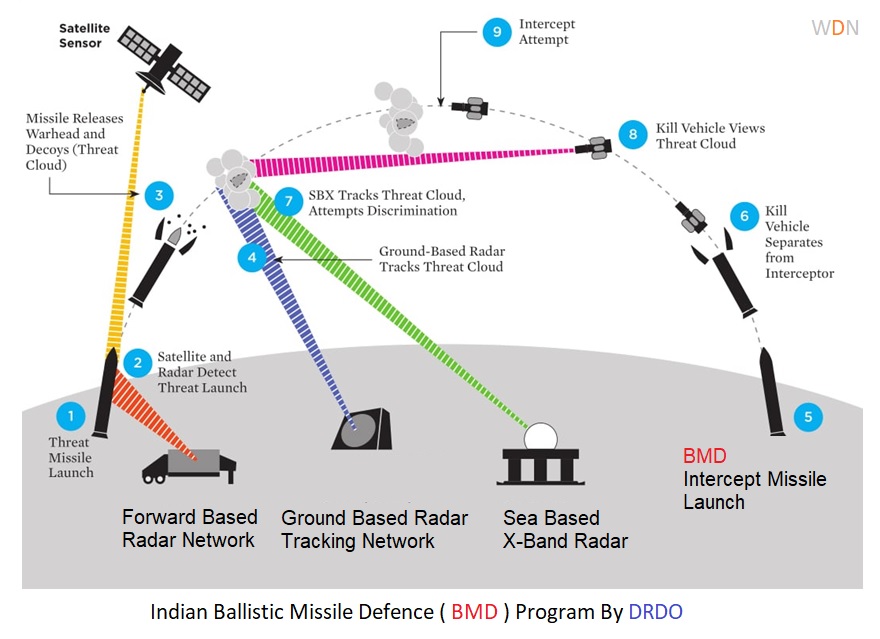
The Indian BMD system is designed to track and intercept incoming nuclear or non-nuclear ballistic missiles at different stages of their flight. The system components include network of powerful radars to track and identify potential threats and different types of interceptor missiles.
The DRDO has developed wide range of interceptor missiles, such as the Prithvi Air Defence (PAD) missile for high altitude interception, the Advanced Air Defence (AAD) missile for lower altitude interception, and the PDV (Prithvi Defence Vehicle) missile for exo-atmospheric interception. The BMD system components also includes radars, tracking systems, missiles batteries and command and control posts.
The Indian BMD program already partially operational and has achieved several successful tests in recent years. In 2019, India successfully tested the PDV missile, which demonstrated the capability of intercepting targets at exo-atmospheric altitudes. In addition, the system has been deployed to protect important cities and strategic locations in India.

However, the Indian BMD program has also faced some criticism and skepticism from experts although BMD is a defensive program. The development hypersonic missiles have raised concerns about the reliability and effectiveness of the system, as well as its cost and technical challenges. Nonetheless, the Indian government has accorded top priority and remains committed to the BMD program as a key component of its defense strategy.
As per the latest Ministry Of Defense press release dated 21st April 2023 , India’s BMD program has achieved another important milestone by successfully intercepting incoming ICBM with the help of sea based launch platform.
Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and Indian Navy successfully conducted a maiden flight trial of sea-based endo-atmospheric interceptor missile off the coast of Odisha in the Bay of Bengal on April 21, 2023. The purpose of the trial was to engage and neutralize a hostile ballistic missile threat thereby elevating India into the elite club of Nations having Naval BMD capability.
DRDO has already successfully demonstrated the capabilities of the land-based BMD system to neutralize ballistic missile threats, emerging from adversaries.
Indian Defense Minister Shri Rajnath Singh congratulated the DRDO team, Indian Navy and Industry involved in this successful technology demonstration of ship based Ballistic Missile Defense system.
How Ballistic Missile Defence System Works ?
Ballistic Missile Defense (BMD) is a system designed to detect, track, and intercept incoming ballistic missiles, typically nuclear missiles, in order to protect against attacks from adversaries. The main objective of the BMD system is to intercept and destroy the incoming missile before it reaches its target. The BMD system is highly effective measure to minimize the risk of potential damage and casualties that a nuclear missile strike could cause.
A ballistic missile follows a predictable path as it travels through space, known as its ballistic trajectory. The BMD systems make use of various system components to track and intercept the missile at different stages of its flight. These system components may include radar systems, satellite surveillance, infrared sensors, command control post and interceptor missiles.
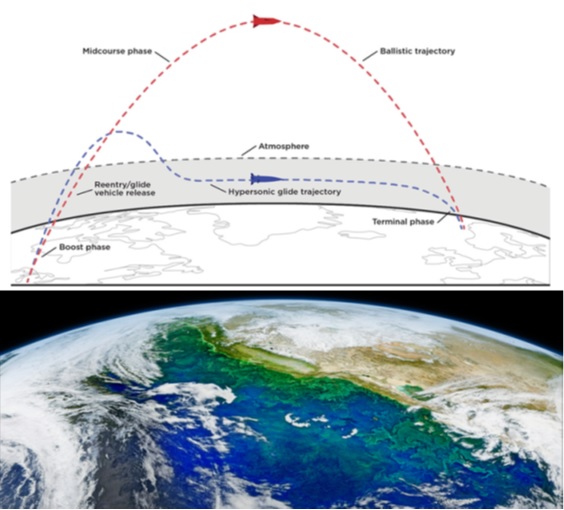
BMD systems can be deployed on land, at sea, or in space. The system can be integrated with other defense systems, such as air defense systems, to provide comprehensive protection against a range of threats.
BMD has become an integral part of national defense strategies for countries around the world, especially in regions where ballistic missiles are a significant threat. However, the development and deployment of BMD systems can be complex, costly, and technically challenging project. Advent of hypersonic missiles have reduced the reaction time to bare minimum. Therefore, there is ongoing debate about the effectiveness and practicality of these systems.
China-Pakistan Nuclear Program And Indian Credible Minimum Deterrence
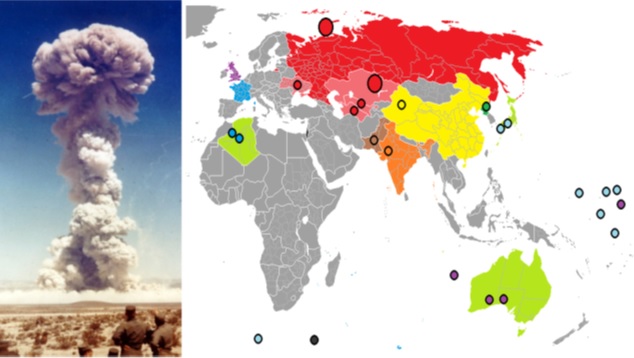
The Chinese and Pakistani nuclear missile arsenals are considered a serious threat to India’s security. Pakistani leaders have threatened India of nuclear attack on Indian cities. Both these countries have a history of strained relations with India and have made statements regarding their nuclear capabilities that suggest they view India as a potential target.
China became the first Asian country to develop nuclear weapon. China possesses a formidable nuclear arsenal, including intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) capable of striking India. Further, China has been rapidly expanding its nuclear capabilities and has tested hypersonic weapons that are believed to be capable of evading existing missile defense.
China has also provided Pakistan with significant support in its nuclear program, including the transfer of nuclear technology and weapon grade materials. Pakistan’s nuclear arsenal is estimated to be smaller than China’s, but it still poses a significant threat to India.
Pakistan has developed short-range nuclear-capable missiles, such as the Hatf-IX (Nasr), which is designed to target Indian troops in a battlefield scenario. Pakistan also possesses medium-range ballistic missiles, such as the Ghauri and Shaheen, which can reach many major Indian cities.
Furthermore, India has committed and declared a “no first use” policy regarding nuclear weapons, which means that they will only use them in response to a nuclear attack. Whereas, both China and Pakistan have not adopted any such “no first use” policy regarding nuclear weapons. As such both China and Pakistan reserves the right to use nuclear weapons in response to a conventional attack.
Therefore, China- Pakistan Strategic alliance and combination of China’s advanced nuclear capabilities and Pakistan’s proximity to India and its possession of nuclear weapons pose a serious threat to India’s security.

